A Beginner’s Guide to Stock Trading: Tips, Insights, and Strategies for Success

Stock trading offers the potential for substantial financial growth, yet it can also be overwhelming for beginners. With a multitude of strategies, trading platforms, and analytical tools available, it’s easy to feel lost at the start. While many new traders enter the market each day, only a fraction reach their full potential. This often happens due to insufficient preparation, lack of knowledge, and poor risk management. The good news? With the right mindset, tools, and a strategic approach, anyone can master the art of stock trading and unlock the potential for significant returns.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand your trading style: Whether you’re drawn to short-term trades or long-term investments, your style should align with your personality, risk tolerance, and available time.
- Choose the right brokerage: Pick a platform that suits your trading style and offers the necessary tools, support, and educational resources.
- Leverage both fundamental and technical analysis: These two critical types of analysis provide the insight needed to make sound, informed decisions.
- Master order types: Learn about various order types (e.g., limit, market, stop-loss orders) to mitigate risks and make precise decisions.
- Develop a risk management strategy: This includes setting position sizes, using stop-loss orders, and maintaining a diversified portfolio to safeguard against significant losses.
How to Trade Stocks: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners

Trading stocks isn’t just about buying and selling; it’s about understanding the market, knowing your risk tolerance, and using strategies that fit your financial goals. To become a successful trader, you need to reflect on your personality, available time, and capacity for risk. Here’s how to get started:
Step 1: Decide What Type of Trader You Want to Be
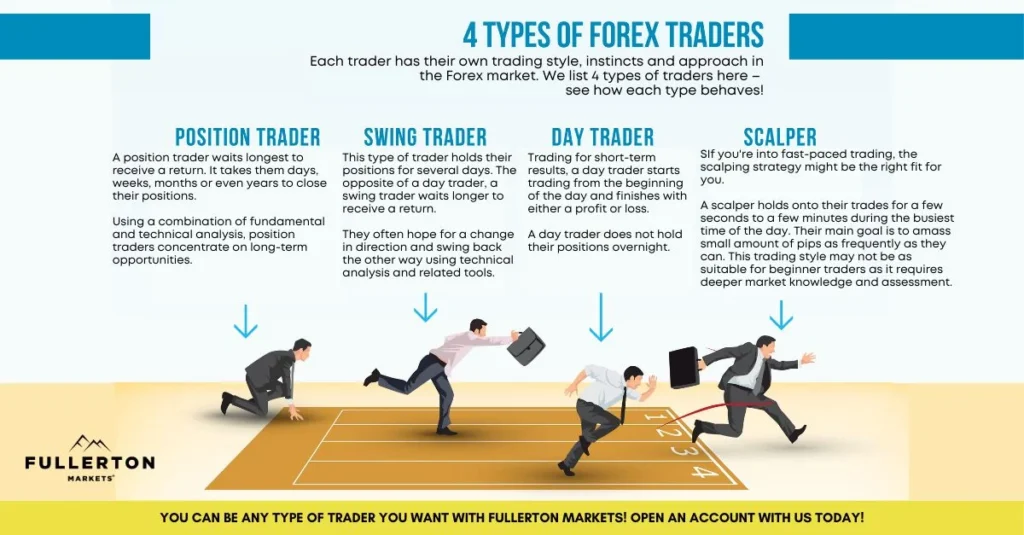
The first step is understanding what kind of trader you are. Different types of trading appeal to different personalities and financial goals. Here are the key types of trading:
- Day Trading: This is the most fast-paced form of trading, where traders buy and sell stocks within the same day, capitalizing on small price movements. Day trading requires a solid understanding of technical analysis, quick decision-making, and substantial time commitment.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, aiming to profit from short- to medium-term price movements. This strategy involves more patience than day trading and typically requires a mix of technical and fundamental analysis.
- Position Trading: This is a long-term approach where traders hold stocks for months or years, based on fundamental factors. Position traders rely heavily on company fundamentals and macroeconomic trends rather than market timing.
- Scalping: A subset of day trading, scalpers make small, frequent trades to capture tiny price changes. This requires a high level of skill, quick thinking, and a high tolerance for risk.
- Long-Term Investing: This approach involves purchasing stocks with the intention of holding them for several years. Long-term investors often focus on stable, established companies and are less concerned with short-term fluctuations.
Your trading style should be aligned with your risk appetite, time availability, and long-term financial goals.
Step 2: Choose the Right Brokerage Platform

Picking the right brokerage is crucial for your success in stock trading. Not all platforms are created equal, and the right one for you will depend on your trading style. Here are some features to look for:
- Low Fees: Transaction fees can eat into your profits. Choose a platform that offers low commissions, especially if you’re an active trader.
- Trading Tools: A good platform will provide a range of tools such as charting, real-time data, and access to advanced technical analysis tools. If you’re a beginner, ensure the platform has user-friendly features and educational resources.
- Support and Education: Many brokers offer educational resources such as webinars, tutorials, and 24/7 customer support. These can be invaluable, especially in the early stages of your trading journey.
- Account Types: Make sure the platform offers a variety of account types (individual, retirement, joint accounts) to match your trading needs and goals.
Popular trading platforms include E*TRADE, Fidelity, TD Ameritrade, and Webull, each offering varying levels of tools, support, and fees.
Step 3: Understand Fundamental and Technical Analysis
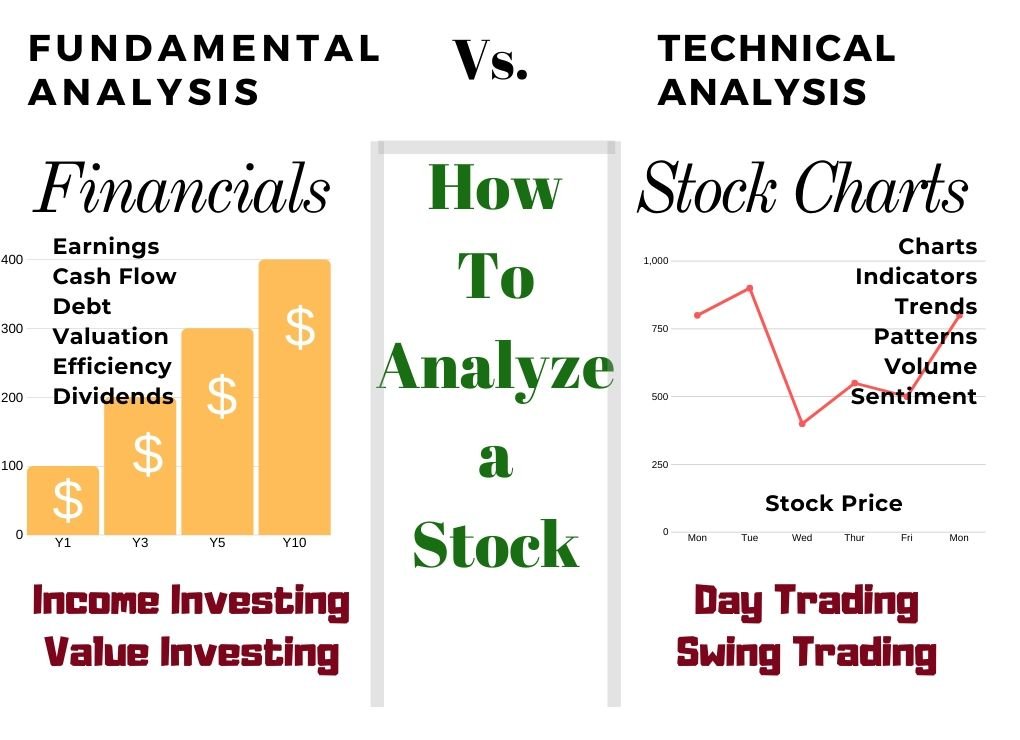
In order to make informed decisions, stock traders rely on two main types of analysis: fundamental and technical. Both play crucial roles in trading strategies.
- Fundamental Analysis: This involves analyzing a company’s financial health, performance, and potential for future growth. Key indicators include earnings reports, revenue growth, debt levels, and market conditions. Fundamental analysis is crucial for long-term investors and position traders.
- Technical Analysis: This focuses on stock price movements, trading volume, and chart patterns. Traders use historical price data to forecast future movements. Key tools include candlestick charts, moving averages, and oscillators. Technical analysis is essential for day traders and swing traders who rely on price movements and trends.
By combining both methods, you can get a comprehensive view of a stock’s potential and make better-informed decisions.
Step 4: Learn About Order Types and Risk Management
Stock traders use various order types to control their entry and exit points, manage risk, and enhance their decision-making. Here are the most common order types:
- Market Orders: These orders buy or sell stocks at the current market price. They’re ideal for entering a trade quickly, but they don’t guarantee the price you’ll receive.
- Limit Orders: These orders specify the maximum price you’re willing to pay to buy, or the minimum price you’re willing to accept to sell a stock. Limit orders help you avoid paying more than you intend, but they may not always be filled.
- Stop-Loss Orders: These orders automatically sell a stock when it falls below a certain price, helping you limit potential losses. This is crucial for protecting your portfolio from large downturns.
- Trailing Stop Orders: A more advanced risk management tool, these orders follow the stock’s price movements, automatically adjusting the stop-loss level as the price rises.
Risk management is essential to protect your capital. You should never risk more than you can afford to lose on a single trade. Additionally, use diversification to spread your investments across multiple sectors, reducing the impact of a single poor-performing stock.
Step 5: Practice, Monitor, and Adjust

Like any skill, stock trading improves with practice. Many platforms offer demo accounts, which allow you to practice without real money on the line. This is an excellent way to familiarize yourself with the tools and test out strategies before you go live.
Once you start trading with real capital, monitor your trades regularly. Keep track of your wins and losses, and assess whether your strategy is working. Don’t be afraid to make adjustments to your approach as you gain more experience.
Step 6: Stay Disciplined and Patient

Stock trading requires discipline and patience. It’s easy to get swept up in market hype or chase quick profits, but successful traders know that consistency and a long-term perspective yield the best results. Stick to your strategy, avoid emotional decisions, and remember that losses are a natural part of trading. Over time, your skills and confidence will grow, and so will your potential for success.
Conclusion: Begin Your Stock Trading Journey with Confidence
While stock trading can seem complex, taking a methodical approach can increase your chances of success. Focus on understanding your trading style, choosing the right tools, and employing risk management strategies to safeguard your investments. With patience, preparation, and consistent practice, you can build the skills needed to succeed in the exciting world of stock trading. Whether you’re looking to make short-term profits or build long-term wealth, remember that knowledge, discipline, and strategy are your keys to success.